There are mainly three types of array.these are follows.
by the above statement we are giving an integer type are array named a which can store the element up to 10. In the declaration of an array three things must be encountered:
The element of A first subscript J and second subscript K will be denoted by
These are all the operation of the array. Now we will be discuss operation one-by-one.- One- Dimensional array
- Two- Dimensional array
- Multi- Dimensional array
by the above statement we are giving an integer type are array named a which can store the element up to 10. In the declaration of an array three things must be encountered:
data-type var_name[size];
We can calculate the length of an array using the given formula:
Length=(UB-LB)+1
LB=Lower bound
UB=Upper bound
Here we have used '+1' in the formula since in general an array is started from 0 location and to find the exact location of the number '+1' is applied.
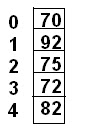
Example :Let we have marks of 5 students then it can be show as follows:
Marks[0]=70, Marks[1]=92, Marks[2]=75, marks[3]=72, Marks[4]=82,
It can be display in row from of array as follows:
And in column from as follows:
Hence we can calculate the length of this array.
Length = (UB+LB)+1
=4-0+1
=5
Memory allocation to an array:~As per the data type of the element it is allocate memory space i.e. in C for int 2 bytes, for char 1byte etc.So for the generalized memory space we can drive the expression for each kind data type.
Memory space Required= Length*w
w = byte allocated to that type of data type
For e.g. if we take above given example then from formula
memory apace Reuired = Length*w
(for int w=2)
=5*2
=10
This array will occur 10bytes in memory
Let LA be a liner array in the memory of the system. So we can calculate the location of element in the follows manner.
LOC(LAK)=Base(LA)+W(K-lower bound)
Where LA is the linear array, Base address(LA) is denoted the address of the first element of LA and W is the number of words for memory cell for the array LA.
Example: consider an array school, which record the number of school generated each year from 1947 to 1999. Suppose SCHOOL appears in memory as picture-
W=4 words per memory cell for SCHOOL
LOC [1947]=500, LOC[1948]=504,...............
So find the address of array element for the year =1980, So
LOC(SCHOOL[1980]) =Base (SCHOOL)+W(1980-LB)
=500+4(1980 - 1947)
=632
Two dimensional array : A two dimensional array m * n array is a collection of m.n data elements such that each element is specified by a pair of integers data type, called subscript.The element of A first subscript J and second subscript K will be denoted by
Aj,k or A[J,K]
Notes-Detailed study of 2-D array will cover in the next post.
Multi- Dimensional array :-General Multidimensional array are defined analogously an n-dimensional array M1 * M2 *M3....................Mn, array B is a collection of M1 * M2 *M3....................Mn, data elements can be represents as:
Bk1,k2.......kn or B[k1 k2.......kn]
Operation of array
There are many operation perform by the linear array, there are as follows:
- Traversal the array
- Deletion from an array
- Sorting is an array
- Insertion in an array
- Searching in an array
- Merging in an array
- Traversal the array :-By traversing we mean, accessing and/or processing(visiting) of each element exactly once of the array.
- [ Initialize counter] Set K=LB
- Repeat step 3 and 4 while K<=UB
- [Traverse an element] Apply process to LA[K]
- [Increase counter] set K=K+1
- [End of the step 2 loop]
- Exit
Program:-
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main() /* Main function */
{
int a[10], i;
clrscr();
printf("enter array value");
for(i=0; i<10; i++)
{
scanf("%d", & a[i])
}
printf("the enter array is/n");
for( i=0;, i<10; i++)
{
printf("%d",a[i]);
}
getch();
}
Output of program:-
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
The enter array is
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9



No comments:
Post a Comment